Search results (248)
Skip results of view Data stories
- Data Story
The European data strategy sets out the vision of creating a single market for data where it can flow freely within the EU and across sectors. The creation of EU-wide, common, interoperable data spaces in strategic sectors is a pillar of the data strategy and will help overcome existing technical and legal barriers to data sharing and unleash the potential of data. These data spaces will bring...
- Data Story
The farm-to-fork strategy is one of the pillars of the European Green Deal , which strives to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent. In this regard, the farm-to-fork strategy strives to accelerate the European Union’s transition to a sustainable food system. A sustainable food system includes schemes such as creating a sustainability labelling framework that aligns with other initiatives...
- Data Story
The European Union implemented a new trade policy in 2022, aiming to transform its economy. This policy represents a shift towards an economy that is robust and responsive, focusing on three main goals: supporting the EU’s economic recovery, aligning with green and digital initiatives, and reshaping global trade for fairness and sustainability. Data is crucial for comprehending the complexities of...
- Data Story
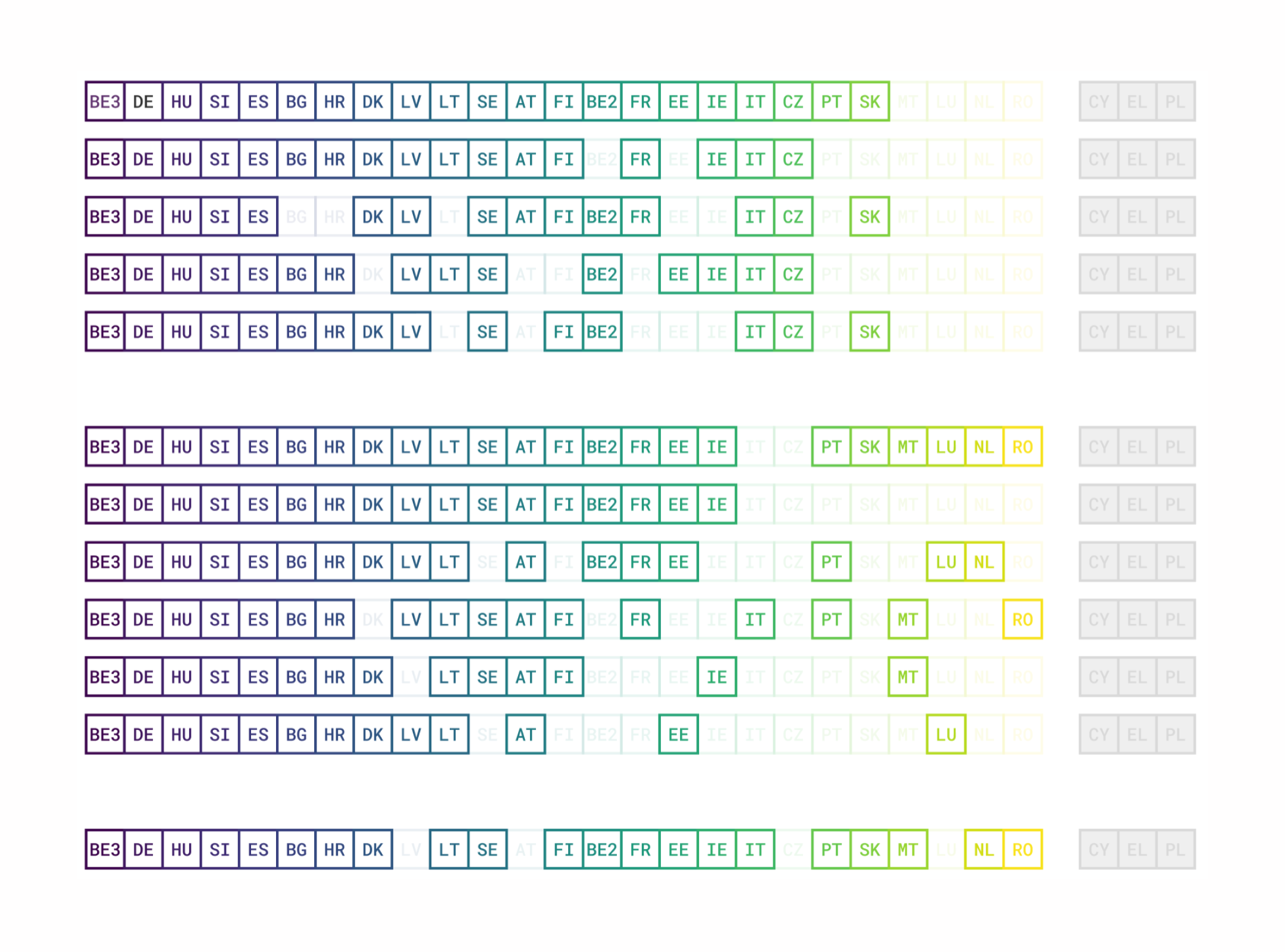
The open data maturity (ODM) assessment by data.europa.eu measures the progress of European countries in making public sector information available and stimulating its reuse. The results show the level of maturity of the participating countries and support the development and sharing of best practices regarding open data across Europe. A total of 35 countries participated in the ninth consecutive...

- Data Story
Three leading institutions are involved in EU decision-making. The European Parliament represents EU citizens, the Council of the European Union represents EU governments, and the European Commission represents the EU’s overall interests. The Council of the European Union comprises government ministers from each EU Member State, who make decisions on EU laws jointly with the European Parliament...
- Data Story
This data story explores family spending by using official EU bodies’ data. The analysis of family budgets reveals the complexities involved in household financial decision-making and identifies key trends in family spending. Each expenditure, whether on necessities or discretionary items, contributes to understanding a broader economic landscape by showing disparities across different...

- Data Story
The European Drug Report is an annual report on the drug situation in Europe published by the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) , an agency of the European Union. It provides an overview of the current drug landscape in Europe, focusing on aspects such as illicit drug consumption, associated risks and drug distribution. For the first time, this year’s report was...

- Data Story
In today’s increasingly digital world, protecting the EU’s cyber realm is becoming more and more important to safeguard digital innovation from threats and vulnerabilities. One of the contemporary challenges identified by ENISA in its annual Threat Landscape report (2022) on the state of cybersecurity is the spread of disinformation. The report gives examples on how disinformation online (also...
- Data Story
Digital skills are becoming increasingly essential for both personal and professional life. Currently, more than 90 % of jobs in Europe require basic digital knowledge alongside traditional skills like literacy and numeracy. However, approximately 32 % of Europeans still lack basic digital skills. Given the pervasive role of digital technology in sectors ranging from business to transport to...
- Data Story
Interested in data visualisation? We invite you to explore our Data Visualisation Guide and dive into seven subjects to gain a deeper understanding of various aspects related to visualising data. The guide was created by the Publications Office of the European Union in collaboration with data visualisation expert Maarten Lambrechts. Find out more about the guide’s content and how you can use it in...
