Den Europæiske Dataportal indsamler metadata fra oplysninger om den offentlige sektor på offentlige dataportaler i de europæiske lande. Hertil hører også oplysninger om tilvejebringelsen af data og fordelene ved at videreanvende data.
Åbne (offentlige) data referer til oplysninger, som er indsamlet, produceret eller betalt af offentlige organer (også kaldet offentlig information), og som stilles gratis til rådighed for videreanvendelse til ethvert formål. Anvendelsesbetingelserne er præciseret i licensen. Principperne for åbne data er beskrevet nærmere i Open Definition.
Informationer fra den offentlige sektor omfatter informationer, som den offentlige sektor er i besiddelse af. Direktivet om videreanvendelse af den offentlige sektors informationer tilvejebringer et fælles retsgrundlag for et europæisk marked for de offentlige myndigheders data. Det bygger på de vigtigste søjler i det indre marked: fri udveksling af data, gennemsigtighed og loyal konkurrence. Det er vigtigt at bemærke, at ikke alle den offentlige sektors informationer er åbne data.
Læs mere om PSI-direktivet og andre ikke-lovgivningsmæssige aktiviteter under GD Connect (Generealdirektoratet for Kommunikationsnet, Indhold og Teknologi) inden for dette område.
Fordelene ved at anvende data
Der er mange fordele ved at anvende åbne data, herunder større effektivitet i offentlige forvaltninger, økonomisk vækst i den offentlige sektor samt større social tryghed.
Åbne data kan give bedre resultater og bidrage til at forbedre effektiviteten af offentlige tjenester. Datadeling på tværs af sektorer gør processer og levering af offentlige tjenester mere effektiv, og kan f.eks. give et overblik over unødvendige udgifter.
Økonomien kan styrkes gennem en lettere adgang til informationer, indhold og viden, hvilket igen bidrager til udvikling af innovative tjenester og nye forretningsmodeller.
Den sociale tryghed kan forbedres ,da det er en fordel for samfundet med informationer, der er mere gennemsigtige og tilgængelige. Åbne data styrker samarbejde, deltagelse og social innovation.
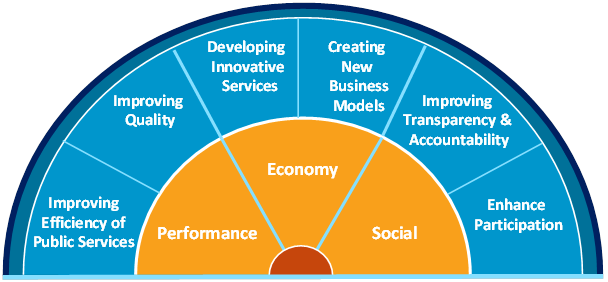
Økonomien kan styrkes gennem en lettere adgang til informationer, indhold og viden, hvilket igen bidrager til udvikling af innovative tjenester og nye forretningsmodeller.
Den direkte markedsandel for åbne data forventes i 2016 at blive 55,3 mia. EUR for EU 28+. Mellem 2016 og 2020 forventes markedsandelen at stige med 36,9 % til en værdi af 75,7 mia. EUR, inklusiv inflationsjusteringer. For perioden 2016-2020 beregnes den kumulative direkte markedsandel til 325 mia. EUR.


Stimuleringen af økonomien og en større efterspørgsel efter medarbejdere, der er kvalificerede til at arbejde med data, vil føre til skabelsen af nye jobs. I 2016 vil der i den private sektor i EU 28+ være 75 000 jobs relateret til åbne data. Inden 2020 vil dette tal øges til lige under 100 000 job relateret til åbne data.. Dette vil skabe næsten 25 000 nye direkte job vedrørende åbne data inden 2020.
Den offentlige sektors ydelser kan styrkes ved anvendelse af åbne data. Datadeling på tværs af sektorer gør processer og levering af offentlige tjenester mere effektiv, da det giver en hurtigere adgang til informationer. De akkumulerede besparelser for EU 28+ i 2020 forventes at blive på 1,7 mia. EUR..

Åbne data giver større effektivitet , da der anvendes realtidsdata. Det giver nem adgang til informationer, hvilket forbedrer den individuelle beslutningstagning. Følgende tre casestudier er beskrevet mere detaljeret: hvordan åbne data kan redde liv, hvordan de kan anvendes til at spare tid, samt hvordan åbne data kan bidrage til at opnå miljømæssige gevinster. Åbne data kan f.eks. potentielt redde 7 000 liv om året , idet de giver mulighed for hurtigere førstehjælp. Anvendelse af åbne data i trafikken kan spare 629 millioner timers unødig ventetid på de europæiske veje.
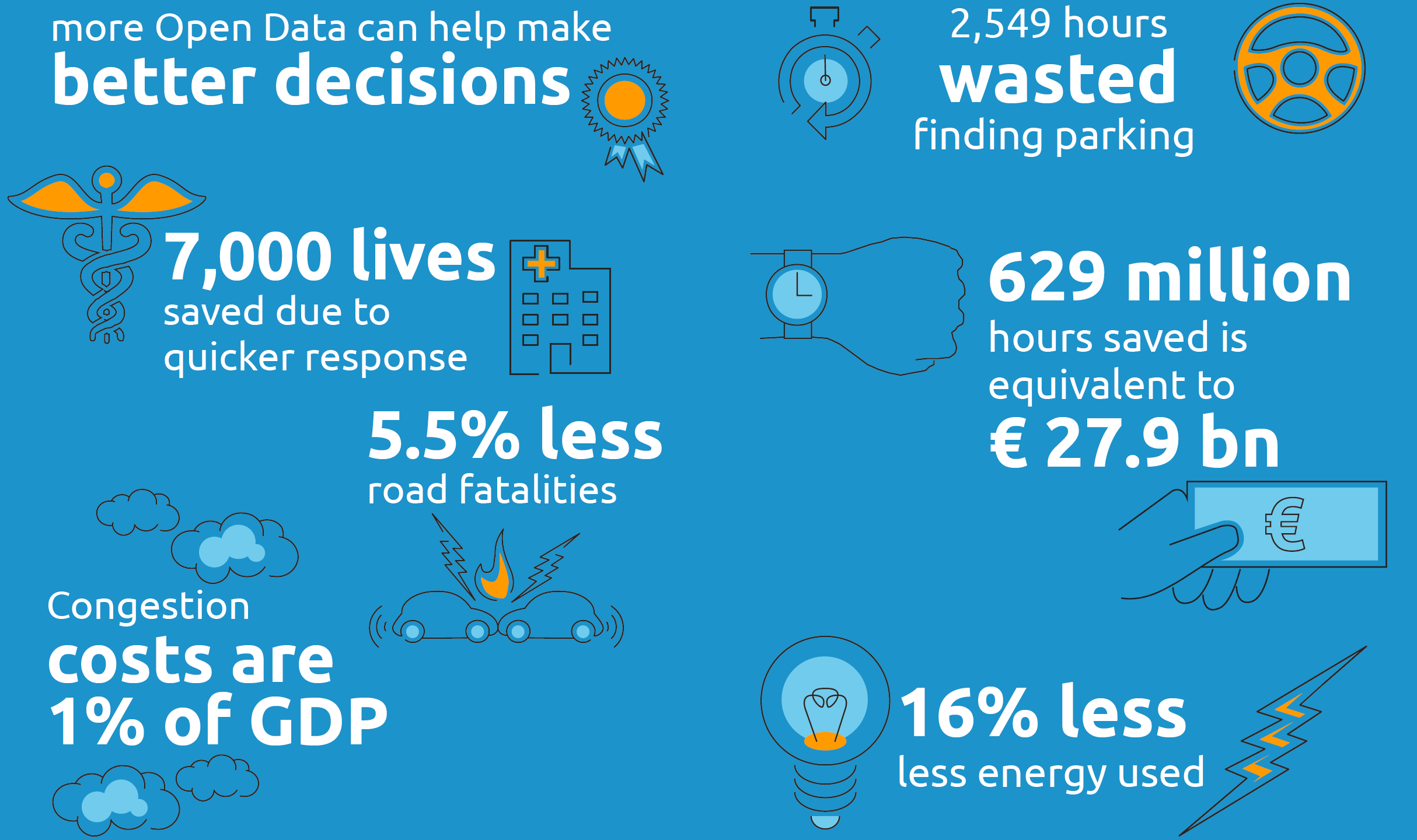
En sammenfatning af resultaterne af det økonomiske studie om fordelene ved åbne data kan læses her:
Tjekliste for anvendelse af data
Important steps to go through before using the data.
Having access to data is a first step. Data is not an end in itself. Data can be used in different ways and for different purposes. Data can also be available with different licences, formats and quality.
Your purpose
Define your purpose: There are different purposes for which the use of Open Data can add value to your activities. It can provide insight into a specific topic that you want more information about or even write about (i.e. data journalism). Open Data can also add required information to an application or service, like details about schools if you are developing an application to help find the best school for yourself or your children. Businesses can also use Open Data to improve their customer profiles and are able to fit the needs of their customers better. Whether it is for private or commercial use, Open Data offers a lot of possibilities.
Identify Data labels: If you know for which purpose you need data, it is important to look whether the data fits your needs by looking at the data labels and metadata (data about the data). For example, if you want to build an application that gives advice about the best primary education in the neighbourhood, you need to check whether the data set that you would like to use includes schools that give primary education, covers the specific area you want to include and whether performance indicators are available.
Open licence
Check Openness: Take a look at the licence information provided about the data set. Make sure a licence is available which allows you to make use of the data in the way that you intend (e.g. that commercial re-use is allowed if you develop a commercial application).
Check Attribution requirements: It is possible that the licence states that people who use the data must credit whoever is publishing it, which means that you need to credit the owner when you make your product or service available. This is called attribution.
Check Share-Alike requirements: If it indicates that people who mix the data with other data have to also release the results as Open Data, you are obliged to publish your own data under a similar licence after adding other data to the original source. This is called share-alike. Make sure that the licence is in line with your purpose for using the data.
In the absence of a licence, there is no information about the terms and conditions applicable! You may want to contact the owner of the data to check what uses are allowed
File format
After you have decided that a specific data set is exactly what you are looking for, you are probably able to choose to download the datasets in different file formats. Depending on your computer skills, you can choose the file type that is most appropriate. The most common file format for tabular data is ‘.csv’. It allows you to add other information to the file or make calculations with the data. Datasets that can be adjusted are published using an open file format. Most datasets are available in an open file format, but bear in mind that some formats (e.g. ‘.pdf’) are not changeable.
Data Quality
On the page where you want to download the data set, you should find information about the last date the file was modified. If you require data for a specific period of time, you need to check whether information about the time period is provided or it has been updated recently. You should check whether the information you were expecting to find in the file is actually included and you understand the different labels.
Here is a short checklist developed by the Open Data Institute:
Form
- how has the data been processed?
- is it in raw or summary form?
- how will its form affect your analysis/product/application?
- what syntactic (language) and semantic (meaning) transformations will you need to make?
- is this compatible with other datasets you have?
Quality
- how current is the data?
- how regularly is it updated?
- do you understand all the fields and their context?
- for how long will it be published?
- what is the commitment by the publisher?
- what do you know about the accuracy of the data?
- how are missing data handled?
Look around at data.europa.eu and discover how it fits your data needs.
